In an era where urbanization and industrialization have reached unprecedented levels, the issue of air quality has become more pressing than ever. For many of us, the air we breathe is an afterthought, something we take for granted as we go about our daily lives. However, growing evidence suggests that the quality of air not only impacts our environment but significantly influences our health and overall well-being. From respiratory diseases to cardiovascular conditions and even mental health issues, the effects of air pollution are far-reaching and often insidious.
As we strive for a healthier lifestyle, understanding the intricate relationship between air quality and our health is crucial. In this article, we will explore the science behind air pollutants, delve into the short- and long-term effects of poor air quality, and discuss practical steps you can take to protect yourself and your loved ones. By bringing awareness to this hidden threat, we hope to empower you to make informed decisions for your health and contribute to a cleaner, safer environment for all.
Table of Contents
- The Science Behind Air Quality and Its Impact on Health
- Common Pollutants and Their Specific Health Risks
- Effective Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality
- Outdoor Air Quality: Awareness, Monitoring, and Personal Responsibility
- Wrapping Up
The Science Behind Air Quality and Its Impact on Health
The intricate relationship between air quality and health is supported by a wealth of scientific research. Poor air quality can lead to a range of health issues, primarily impacting the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Particulate matter (PM), ozone, and nitrogen dioxide are among the most common pollutants that, when inhaled, can initiate or exacerbate diseases such as asthma, bronchitis, and heart disease. Specifically, fine particulate matter (PM2.5) can penetrate deep into the lungs and even enter the bloodstream, leading to systemic inflammation and other serious health implications.
The effects of air pollution extend beyond immediate health concerns, influencing longer-term well-being. Populations living in areas with high levels of air pollutants often experience higher rates of chronic diseases, increased healthcare costs, and diminished quality of life. Interestingly, researchers have found links between air quality and mental health, suggesting that sustained exposure to high pollution levels may contribute to conditions like depression and anxiety. Awareness of these risks empowers individuals to make informed choices about their environment and advocate for policies aimed at improving air quality.
| Pollutant | Health Impact |
|---|---|
| PM2.5 | Respiratory issues, cardiovascular diseases |
| Ozone (O3) | Asthma exacerbation, lung inflammation |
| Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) | Increased risk of respiratory infections |
Common Pollutants and Their Specific Health Risks
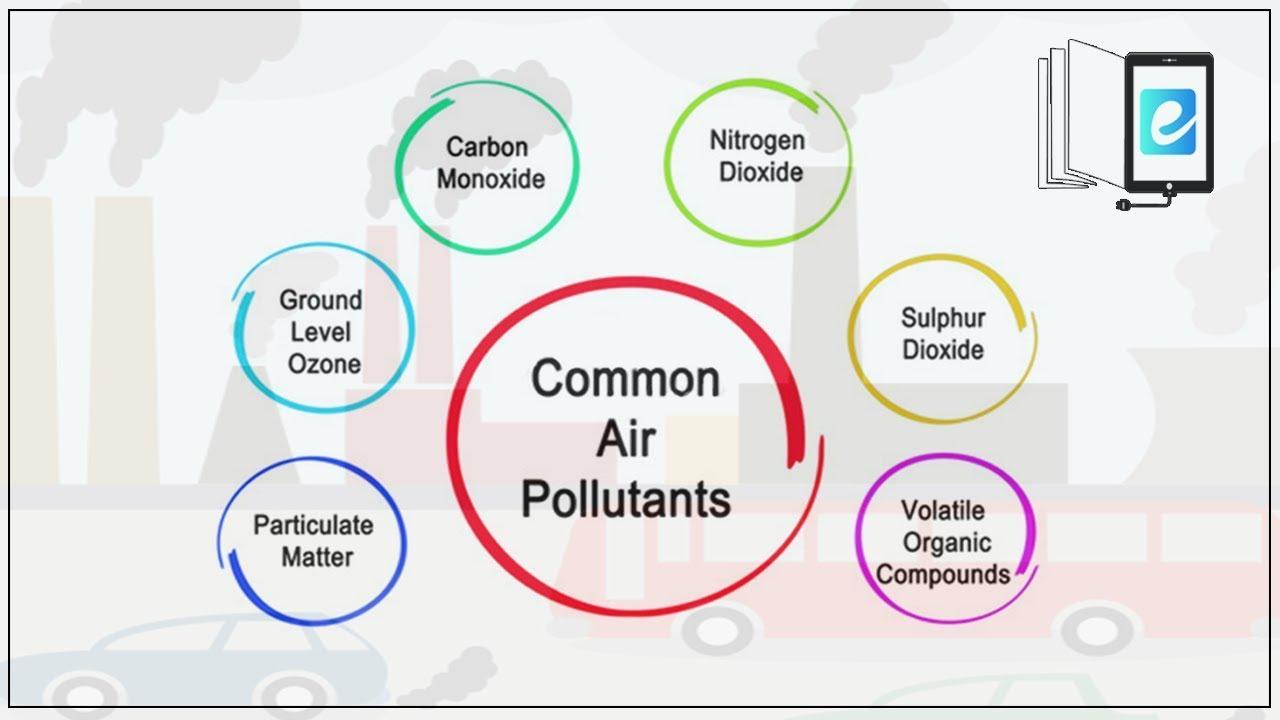
Air quality is compromised by various pollutants that pose significant health risks, impacting both short-term and long-term well-being. Among the most common offenders are particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), which can penetrate deep into the lungs and enter the bloodstream. These minuscule particles are linked to serious respiratory issues such as asthma attacks and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), as well as cardiovascular problems. Another notorious pollutant is nitrogen dioxide (NO2), primarily emitted from vehicle exhaust and industrial activities, which can irritate the airways and has been associated with heightened asthma symptoms and reduced lung function, particularly in children.
In addition to particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, the presence of ozone (O3) presents unique health challenges. Ground-level ozone, formed when sunlight reacts with pollutants, can exacerbate respiratory conditions and lead to symptoms like chest pain and throat irritation. Furthermore, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), released from paints, solvents, and fuels, contribute not only to air pollution but can also cause headaches, dizziness, and long-term nervous system damage. Understanding these pollutants’ specific health risks is crucial for making informed decisions about our environment and advocating for better air quality standards.
| Pollutant | Health Effects |
|---|---|
| Particulate Matter (PM2.5/PM10) | Respiratory illness, cardiovascular problems, lung cancer |
| Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) | Asthma exacerbation, decreased lung function |
| Ozone (O3) | Chest pain, throat irritation, worsened asthma |
| Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) | Headaches, dizziness, long-term nervous system damage |
Effective Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is essential for enhancing overall health and well-being. One effective strategy is to incorporate greenery into your home. Plants like spider plants, peace lilies, and snake plants can naturally filter toxins and improve oxygen levels. Additionally, regularly ventilating your living spaces by opening windows or using exhaust fans helps to circulate fresh air, reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants. Make sure to also monitor humidity levels by using a dehumidifier or humidistat, as maintaining an optimal humidity range of 30-50% can drastically improve air quality and comfort.
Another approach is to reduce the sources of indoor air pollution. This can be achieved by implementing a no-smoking policy in your home and choosing low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) paints and furnishings. Regularly cleaning surfaces, vacuuming with HEPA filters, and using air purifiers can also help capture airborne contaminants. performing an annual inspection of your home’s heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system will ensure that your air ducts are clean and functioning properly, thereby promoting better airflow and air quality.
Outdoor Air Quality: Awareness, Monitoring, and Personal Responsibility
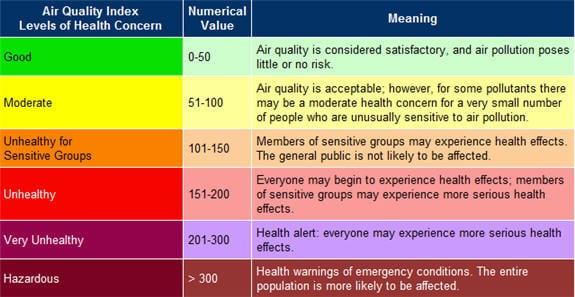
Outdoor air quality has a direct impact on our health and well-being, yet many remain unaware of the environmental factors contributing to pollution. By being informed about local air quality conditions, individuals can understand when to limit outdoor activities, particularly during high pollution days. Local air quality indexes (AQI) serve as essential tools in this regard, providing critical information about the level of pollutants in the atmosphere, which can include:
- Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) – Tiny particles that can penetrate deep into the lungs.
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) – Often a byproduct of vehicle emissions.
- Ground-level ozone (O3) – Formed when pollutants react in sunlight.
To take charge of our health, we must embrace a culture of monitoring and responsibility. Easy access to air quality data empowers individuals to make informed choices about outdoor activities. Additionally, there are personal measures we can adopt to reduce our carbon footprint and enhance outdoor air quality, such as:
- Using public transportation – Reducing emissions from personal vehicles.
- Supporting green initiatives – Planting trees and advocating for clean air policies.
- Educating others – Spread awareness about the importance of air quality.
Here’s a quick overview of how different pollutants affect health:
| Pollutant | Health Impact |
|---|---|
| PM2.5 | Respiratory and cardiovascular diseases |
| NO2 | Worsens asthma and lung inflammation |
| Ozone | Causes throat irritation and shortness of breath |
Wrapping Up
understanding how air quality impacts our health and well-being is more than just an academic exercise; it’s a vital part of our daily lives. By recognizing the sources and effects of air pollution, we empower ourselves to make informed choices and advocate for cleaner air in our communities. Whether it’s reducing exposure by staying indoors on poor air quality days, supporting policies aimed at improving environmental standards, or simply being more aware of the air we breathe, each step we take can contribute to a healthier future for ourselves and for generations to come.
As you reflect on the information shared in this article, consider integrating small, actionable changes into your lifestyle that promote better air quality—both indoors and outdoors. Together, we can foster a healthier environment, reclaim our right to clean air, and ultimately enhance our overall well-being. Your health is worth it, and every effort counts. Thank you for joining us on this critical exploration of air quality and its profound effects on health. Stay informed, stay safe, and breathe easy!