In the intricate tapestry of ecosystems, a delicate balance exists, woven from the threads of life that bind together the flora and fauna of our planet. Each plant and animal, in its own right, plays a vital role in maintaining the symphony of life, a harmonious interplay where strengths are shared, and survival is interlinked. From the towering trees that cradle the nests of vibrant birds, to the humble bee that dances from flower to flower, pollinating as it goes, the connections between flora and fauna are a testament to nature’s artistry. This article embarks on an explorative journey into the heart of these symbiotic relationships, revealing how every leaf, paw, and wing contributes to the broader narrative of coexistence, resilience, and ecological balance. Join us as we delve into the fascinating world of “Symbiotic Harmony,” where life is not merely lived but shared in a wondrous interconnectedness.
Table of Contents
- Exploring Mutual Benefits: How Flora and Fauna Thrive Together
- Ecosystem Services: The Essential Roles of Plant and Animal Partnerships
- Societal Impacts: Balancing Conservation and Development in Natural Habitats
- Cultivating Connections: Strategies for Promoting Biodiversity in Urban Spaces
- Final Thoughts
Exploring Mutual Benefits: How Flora and Fauna Thrive Together

In nature, the intricate dance between plants and animals unfolds a narrative of mutual survival that is both fascinating and vital. The simple act of flowering not only brightens landscapes but also lures pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, which in turn facilitate reproduction by transferring pollen. This partnership goes beyond the act of pollination; it is a tripartite connection where other creatures such as hummingbirds and bats play their roles, ensuring genetic diversity among plant populations. In return, flora provides these creatures with sustenance through nectar, pollen, and even shelter, creating a vibrant ecosystem reliant on shared resources.
Similarly, the relationships between larger fauna and flora are equally compelling. Consider herbivores that graze on grass and foliage; through their feeding habits, they stimulate plant growth, promoting the emergence of fresh shoots that benefit both the plant species and the grazers themselves. This interdependence can also be seen in mutualistic relationships like those of ants and acacia trees, where ants defend the tree from herbivores, while the tree provides them with food and housing. These interactions underscore the importance of biodiversity, illustrating how the health of both flora and fauna is intertwined, thriving through collaboration and shared goals.
Ecosystem Services: The Essential Roles of Plant and Animal Partnerships
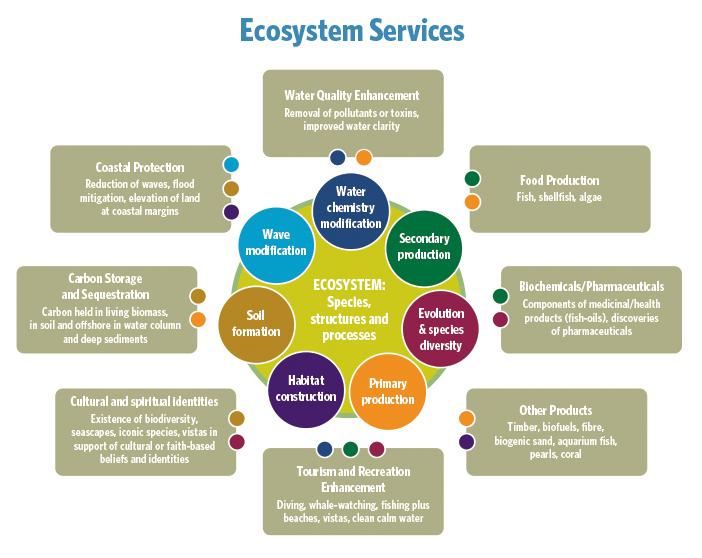
In the intricate tapestry of nature, plant and animal partnerships play a pivotal role in sustaining ecosystems and promoting biodiversity. These collaborations can manifest in various forms, ranging from mutualism, where both organisms benefit, to commensalism, where one thrives while the other remains unaffected. Some notable examples include:
- Pollination: Bees and flowering plants; as bees collect nectar, they inadvertently transfer pollen, aiding plant reproduction.
- Seed Dispersal: Birds and fruiting plants; birds consume fruits and carry seeds to new locations through their droppings.
- Protection: Ants and aphids; ants tend to aphids in exchange for honeydew, helping control aphid populations.
These interactions are essential, as they enhance ecosystem resilience and support numerous services. By improving soil health, regulating water cycles, and providing habitats, these symbiotic relationships create a balance that fosters life. The interdependencies formed through these plant-animal connections can be further illustrated in the following table:
| Partnership | Benefits | Ecosystem Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Coral Reefs & Zooxanthellae | Corals gain nutrients; zooxanthellae gain shelter | Supports marine biodiversity & protects coastlines |
| Fungi & Trees | Trees receive water and nutrients; fungi obtain sugars | Enhances forest health & nutrient cycling |
| Bats & Insectivorous Plants | Bats control insect populations; plants receive pollination | Prevents crop damage & supports food webs |
Societal Impacts: Balancing Conservation and Development in Natural Habitats
The challenge of harmonizing ecological conservation with the demands of development requires a multifaceted approach that considers both the resilience of natural habitats and the needs of human communities. Key figures in urban planning and environmental science are increasingly advocating for eco-friendly practices that foster sustainability. Efforts such as creating wildlife corridors, enforcing strict zoning laws, and introducing green infrastructure promote the coexistence of human and wildlife populations. Effective engagement with local communities is crucial; involving them in conservation projects can enhance stewardship and foster an appreciation for the vital roles that local ecosystems play.
Organizations and local governments can adopt a range of strategies to manage this balance, including:
- Community Education: Raising awareness about biodiversity and the importance of conservation efforts can encourage public support.
- Collaborative Planning: Involving various stakeholders—ranging from local residents to environmental experts—in decision-making processes ensures that multiple perspectives are considered.
- Technological Integration: Utilizing modern technologies such as GIS mapping can help monitor ecosystem health while supporting urban development initiatives.
The table below summarizes impactful case studies from around the globe, showcasing how regions have successfully integrated conservation with development:
| Location | Initiative | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Brazil | Amazon Rainforest Conservation | Reduced deforestation rates and increased biodiversity. |
| Netherlands | Water Management Systems | Enhanced flood resilience while protecting aquatic ecosystems. |
| Kenya | Wildlife Conservation Areas | Boosted local tourism and protected native wildlife species. |
Cultivating Connections: Strategies for Promoting Biodiversity in Urban Spaces
Bringing biodiversity into urban environments requires a collaborative approach, where the merge of vegetation and wildlife can flourish side by side. One effective strategy is the use of native plants in landscaping. These plants not only adapt well to local conditions but also serve as essential habitats for various species of insects, birds, and other wildlife. Furthermore, creating green corridors allows for movement among flora and fauna, enhancing genetic diversity and resilience.
In addition to planting strategies, it’s crucial to foster community engagement through activities like urban gardening and wildlife monitoring programs. These initiatives can empower residents to take an active role in supporting local ecosystems. For instance, organizing workshops on native species can equip individuals with knowledge about sustainable practices. Below is a simple overview of some community-driven actions that promote biodiversity:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Native Plant Workshops | Educate locals on planting and maintaining native species. |
| Pollinator Gardens | Create dedicated spaces for bees and butterflies to thrive. |
| Community Clean-Ups | Enhance local habitats by removing invasive species and litter. |
Final Thoughts
In the intricate tapestry of our planet’s ecosystems, the symbiotic relationships between flora and fauna weave a narrative of interdependence that is both profound and essential. Each thread of relationship, whether it be the delicate dance of pollinators and plants or the subtle balance of predator and prey, contributes to the rich biodiversity that sustains life as we know it. As we continue to explore and understand these connections, we are reminded of the importance of nurturing this harmony. The fate of flora and fauna is intertwined, and by fostering a deeper appreciation for their coexistence, we lay the groundwork for a more sustainable future. In witnessing the beauty of this natural partnership, we not only gain insight into the resilience of life but are also inspired to protect and preserve the delicate balance that surrounds us. After all, the health of our planet rests on the symbiotic harmony of its inhabitants, and it is within this unity that we find hope for generations to come.



