In the grand theater of Earth’s geological narrative, few players are as dynamic and transformative as glaciers. These colossal rivers of ice, gliding imperceptibly yet inexorably across the landscape, sculpt the very fabric of our planet’s surface. From the jagged peaks of the Himalayas to the serene valleys of Scandinavia, glaciers leave an indelible mark on the environment, shaping mountains, valleys, and ecosystems in their wake. As they advance and retreat over millennia, they carry with them not just sediments of rock and earth, but also stories etched in the ice—stories of climate change, ecological resilience, and the intricate dance of natural forces. This article delves into the powerful impact of glaciers, exploring their role as agents of change and the profound influence they exert on our world. Join us as we uncover the artistry and the science behind these frozen giants, revealing how they continue to shape Earth’s canvas even in the face of a warming climate.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Majestic Forces of Glacier Formation
- The Role of Glaciers in Shaping Landscapes and Ecosystems
- Understanding Climate Change Through the Lens of Glacier Dynamics
- Preserving Glacial Heritage: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
- Wrapping Up
Exploring the Majestic Forces of Glacier Formation
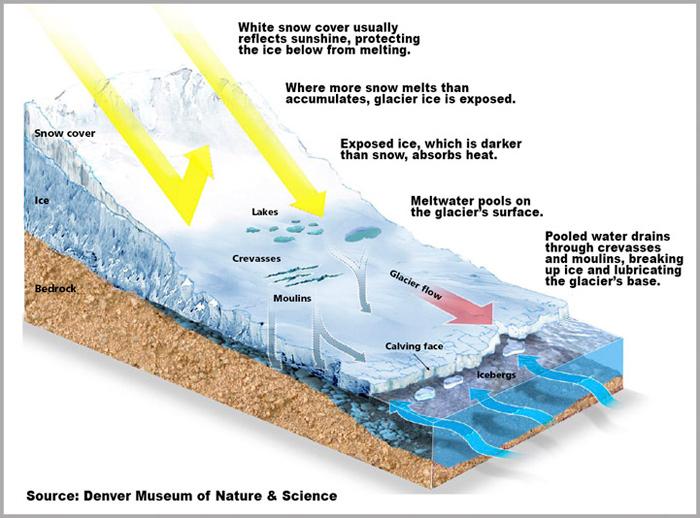
The formation of glaciers is a breathtaking spectacle that embodies the interplay of climate, time, and geological processes. As snow accumulates in layers over years, its weight compacts the lower layers into ice, initiating a slow yet unstoppable journey down mountainsides. The incredible forces at work transform mere precipitation into massive rivers of ice, carving out valleys and shaping the landscape in profound ways. Beyond their breathtaking beauty, glaciers serve as powerful agents of erosion, sculpting the earth’s surface and influencing the ecological balance of their surrounding environments.
To grasp the magnitude of glacier formation, consider the varied factors that contribute to their development:
- Temperature: The delicate balance between cold and warm climates facilitates the accumulation and persistence of snow.
- Altitude: Higher elevations receive more snow, leading to significant glacier growth.
- Geological Conditions: The underlying rock type and topography influence the rate of glacial formation and movement.
| Factor | Impact on Glaciers |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Affects snow melt rate and accumulation. |
| Altitude | Higher elevations encourage glacier formation. |
| Geological Conditions | Shapes glacier movement and erosion potential. |
As these icy titans traverse the land, they not only remind us of nature’s enduring power but also highlight their delicate relationship with their environment. Climate change poses a significant threat to glaciers, as rising temperatures lead to accelerated melting and retreat, altering ecosystems and impacting global sea levels. Understanding the intricacies of glacier formation and the forces behind it is essential for anticipating the potential consequences our planet may face as these majestic formations continue their inexorable retreat.
The Role of Glaciers in Shaping Landscapes and Ecosystems

Glaciers, often referred to as nature’s sculptors, have played a monumental role in the transformation of our planet’s landscapes. As they slowly advance and retreat, these colossal rivers of ice carve through rock and soil, creating a variety of unique geological features. The consequences of their movement include:
- U-shaped valleys: Glaciers deepen and widen valleys, resulting in a distinctive U-shape versus the V-shape formed by rivers.
- Cirques: Bowl-shaped depressions that serve as the source for glacier run-off.
- Moraine formations: Piles of debris left behind as glaciers melt, contributing to the varied topography of the region.
- Fiords: Narrow inlets with steep cliffs, created as glaciers retreat and fill with seawater.
Beyond mere topography, glaciers influence ecosystems by regulating water flow and creating habitats for diverse flora and fauna. As glaciers melt, they release freshwater into rivers, lakes, and wetlands, essential for both human use and the survival of numerous species. The intricate relationship includes:
- Glacial lakes: These bodies of water often support unique aquatic life forms that rely on the cold, nutrient-rich waters.
- Climate regulation: Glaciers act as thermal buffers, maintaining cooler temperatures in adjacent areas.
- Soil formation: The sediments deposited by glaciers provide fertile grounds for various plant species, establishing the foundation for complex ecosystems.
Understanding Climate Change Through the Lens of Glacier Dynamics
Glaciers serve as mesmerizing indicators of climate change, their slow but steady movements intricately woven into the fabric of Earth’s environment. As these colossal ice masses shift, melt, and reform, they offer a tangible narrative of shifting climatic conditions. The dynamics of glaciers reveal critical insights into temperature fluctuations, precipitation patterns, and ultimately, our planet’s health. Understanding these movements not only enlightens us about past climates but also provides a glimpse into potential future impacts, as glaciers are sensitive barometers for environmental changes.
Factors influencing glacier dynamics include a variety of elements, such as:
- Temperature and Melting Rates: Warmer temperatures accelerate melting, leading to reduced ice volume.
- Precipitation Levels: Changes in snowfall can either replenish glaciers or contribute to long-term retreat.
- Topography and Geology: The physical landscape dictates how glaciers flow and interact with their surroundings.
A table illustrating the retreat of notable glaciers over the last few decades emphasizes this point:
| Glacier | Location | Average Retreat (per year) |
|---|---|---|
| Columbia Glacier | Alaska, USA | ~30 meters |
| Mer de Glace | France | ~10 meters |
| Jac glacier | China | ~50 meters |
Each glacier’s retreat sends ripples through nearby ecosystems, affecting water resources and contributing to rising sea levels. By closely examining glacier dynamics, researchers can better predict the cascading effects of climate change, highlighting the urgent need to address environmental concerns before more ice—and with it, crucial biodiversity—is lost forever.
Preserving Glacial Heritage: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
As the world grapples with climate change, the urgency of safeguarding our glacial heritage has never been greater. To address the vulnerabilities of these majestic ice formations, preservation strategies must be multipronged and inclusive. Collaborative efforts between governments, scientists, and local communities are vital to establish protected areas that prevent unsustainable mining, tourism, and industrial practices around glacial zones. Promoting education and awareness through workshops, exhibitions, and digital media can also inspire action and understanding of glaciers’ critical roles as natural reservoirs of freshwater and indicators of climate health.
Furthermore, innovative technological solutions can aid in monitoring and preserving glaciers effectively. Utilization of satellites and drones to gather data on glacial health creates opportunities for real-time assessment and informed decision-making. Communities can engage in sustainable practices by implementing Ecotourism initiatives that balance economic benefits with conservation efforts. To systematically track progress, it’s essential to establish a framework that prioritizes research, community involvement, and adaptive management rooted in the principles of sustainability. Below is a table summarizing key strategies for glacial preservation:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Protected Areas | Designating regions around glaciers to prevent exploitation. |
| Community Engagement | Involving locals in conservation efforts through education. |
| Technology Integration | Using satellite imaging for monitoring glaciers. |
| Ecotourism | Sustainable tourism practices that respect glacial environments. |
Wrapping Up
As we conclude our exploration of the majestic glaciers that carve Earth’s canvas, we are reminded of their duality: both artists and architects of our natural world. Through the slow, relentless march of ice, they shape landscapes, creating valleys and fjords that stand as testaments to their transformative power. While their grandeur enchants and inspires, the tale of glaciers is also one of fragility. As the climate continues to shift, these ancient giants face unprecedented challenges, reminding us of the interconnectedness of our planet and the urgent need for stewardship.
As we reflect on the powerful impact of glaciers, we are called to appreciate the intricate balance of nature and the lessons these icy behemoths provide. They serve as a reminder of time’s passage, the power of persistence, and the delicate threads that hold our ecosystems together. Moving forward, let us carry with us not only the awe that glaciers inspire but also a commitment to understanding and protecting the world they help define—a canvas in constant evolution, shaped by elemental forces and human choices alike. In this intricate dance of nature, we find both beauty and responsibility, urging us to preserve the wonders of our planet for generations to come.



