In the intricate tapestry of nature, every thread plays a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. Among these threads, animals stand out as vital contributors, each species weaving its unique influence into the larger story of life on Earth. From the smallest insects flitting between flowers to the majestic apex predators roaming vast landscapes, the presence and activities of animals shape their environments in profound ways. They act as pollinators, seed dispersers, and natural pest controllers, while also serving as prey for other species within the food web. As human activity increasingly disrupts these ecological networks, the importance of understanding the roles animals play becomes more urgent. This article explores the multifaceted contributions of animals to ecosystem balance, illuminating not only their ecological significance but also the interdependencies that bind all forms of life together. Through this lens, we gain insights into the fragility of our natural world and the essential need for conservation efforts to safeguard these invaluable participants in the ecosystem’s ongoing narrative.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability
- Examining the Impact of Keystone Species in Ecological Dynamics
- Exploring the Interconnectedness of Animal Habitats and Human Well-Being
- Strategies for Promoting Animal Conservation and Ecosystem Health
- In Conclusion
Understanding the Role of Biodiversity in Ecosystem Stability

Biodiversity forms the backbone of ecosystem stability, functioning like a well-oiled machine where each component plays a pivotal role. Wild animals, for instance, actively participate in pollination, seed dispersal, and energy flow, facilitating the smooth operation of various ecological processes. A diverse array of species enhances the resilience of ecosystems, enabling them to withstand disturbances such as climate change, disease outbreaks, or habitat destruction. In essence, a rich tapestry of life fosters a robust network of interdependencies, making the ecosystem adaptable and sustainable even when external pressures mount.
Each species brings unique contributions to its environment, which in turn supports a dynamic equilibrium within the ecosystem. For example, predators such as wolves help control herbivore populations, thus preventing overgrazing and allowing vegetation to flourish. This intricate balancing act can be summarized as:
| Animal Type | Role in Ecosystem |
|---|---|
| Bees | Pollination of plants |
| Wolves | Regulating herbivore populations |
| Birds | Seed dispersal and pest control |
| Earthworms | Soil aeration and nutrient cycling |
By fostering biodiversity, we not only enhance ecosystem resilience but also ensure that critical functions like nutrient cycling and climate regulation are maintained. Recognizing the interconnectedness of all organisms prompts us to protect diverse habitats and preserve species, illuminating our path toward sustainable coexistence with nature.
Examining the Impact of Keystone Species in Ecological Dynamics
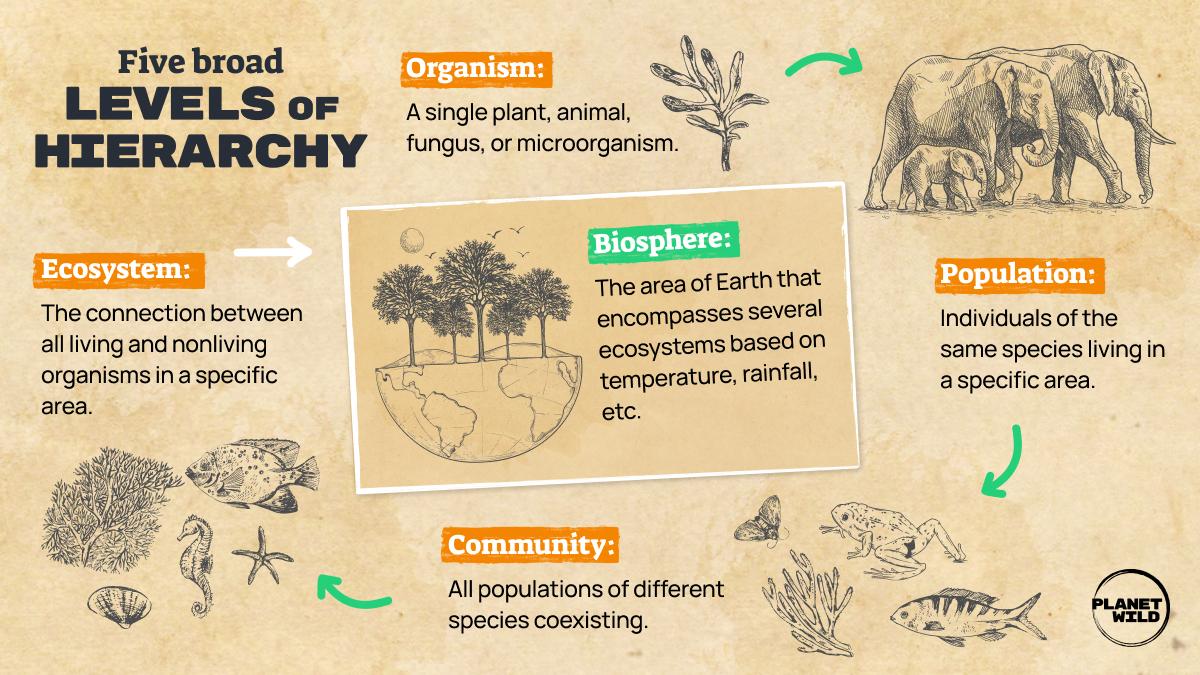
In the intricate web of life, the presence or absence of certain animals can trigger profound shifts within an ecosystem. These dominant organisms, often referred to as keystone species, maintain the structure and integrity of their communities, influencing both the population and composition of other species. For instance, predators such as wolves play a crucial role by controlling the population of herbivores like deer, which in turn allows vegetation to flourish. When wolves are removed, deer populations can explode, leading to overgrazing and a marked decline in plant diversity. This cascade of effects highlights the delicate balance maintained by these vital players.
The contributions of keystone species extend beyond mere population control; they shape entire ecosystems through their behaviors and interactions. Consider the role of beavers as ecosystem engineers. By creating dams, beavers alter water flow, forming ponds that become thriving habitats for a variety of aquatic and terrestrial species. Such changes promote biodiversity, providing a sanctuary for both fish and birds. Below is a concise overview of some notable keystone species and their significant impacts on ecosystems:
| Keystone Species | Role | Ecological Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Wolves | Predator | Regulate herbivore populations; promote plant diversity. |
| Sea Otters | Consumer | Control sea urchin populations; maintain kelp forest health. |
| Beavers | Ecosystem Engineer | Create wetlands; enhance biodiversity through habitat construction. |
Exploring the Interconnectedness of Animal Habitats and Human Well-Being
Throughout the intricate web of life on our planet, the delicate balance of ecosystems is profoundly influenced by the presence of animals. These creatures, ranging from the smallest pollinators to the largest apex predators, contribute significantly to environmental stability and resilience. They perform essential functions such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling, which in turn support plant growth and maintain biodiversity. Without these vital contributors, natural habitats could collapse, leading to a cascade of negative impacts that would ultimately affect human populations. For instance, the decline of bees in agricultural areas has direct consequences on food production, affecting not just local economies but also the global food supply chain.
The interdependence between animal habitats and human well-being extends beyond mere ecosystem services. Healthy ecosystems provide natural resources such as clean water, fertile soil, and medicinal plants, all of which are cornerstones for human survival. Maintaining biodiversity not only safeguards these resources but enhances human quality of life by offering recreational opportunities and promoting mental well-being. In this context, the preservation of animal habitats emerges as a crucial endeavor, not just for the sake of wildlife, but for the sustained prosperity of human societies. Below is a concise table highlighting the interconnectedness between animal functions and human benefits:
| Animal Function | Human Benefit |
|---|---|
| Pollination | Increased crop yields |
| Seed Dispersal | Restoration of plant diversity |
| Nutrient Cycling | Soil fertility enhancement |
| Pest Control | Reduced agricultural losses |
Strategies for Promoting Animal Conservation and Ecosystem Health
To effectively conserve animal populations and promote ecosystem health, it is essential to engage various stakeholders and utilize a multifaceted approach. Community involvement plays a crucial role; local residents can participate in conservation programs that aim to protect regional wildlife and habitats. Education initiatives targeting children and adults alike can foster a greater understanding of animal behaviors and their roles within ecosystems. Health assessments of animal populations can also be prioritized, identifying shifts in species health that may indicate broader ecological changes. Collaboration with indigenous communities often yields invaluable insights into sustainable practices that have preserved local ecosystems for generations.
Technology can enhance conservation efforts significantly. For instance, satellite tracking and drones provide vital data on animal movements and habitat usage, allowing for efficient monitoring of species in the wild. Implementing wildlife corridors can help mitigate risks associated with habitat fragmentation, facilitating safe passage for migrating species. Additionally, policy advocacy aimed at stronger environmental laws can ensure that conservation measures are upheld at governmental levels. The following table summarizes key strategies alongside their intended impacts:
| Strategy | Intended Impact |
|---|---|
| Community Engagement | Fosters local ownership of conservation efforts |
| Technology Utilization | Enhances data collection and monitoring |
| Policy Advocacy | Strengthens protective legislation for wildlife |
In Conclusion
As the sun sets on a landscape woven together by the diverse threads of life, we are reminded of the intricate tapestry that nature has created over millennia. Animals, both great and small, play an essential role in maintaining the equilibrium of our ecosystems. From the silent work of pollinators enhancing plant life to the keystone species that shape entire habitats, their contributions are invaluable.
Throughout this exploration, we’ve uncovered the symbiotic relationships that underscore the interconnectedness of life. Each animal, whether predator or prey, herbivore or scavenger, fills a unique niche that sustains not only their species but countless others as well. The delicate dance between these organisms showcases the profound wisdom of nature—a wisdom that we, as stewards of the Earth, must strive to understand and respect.
As we move forward, it is crucial to recognize our responsibility in preserving these vital contributions. The loss of a single species can reverberate through the ecosystem like ripples in a pond, underscoring the need for conservation efforts and a commitment to biodiversity. By fostering a greater appreciation for the role of animals in our world’s balance, we can inspire a collective action to protect the habitats that support them.
In closing, let us honor the remarkable role animals play in creating and sustaining life on our planet. Their existence transcends mere survival; it is an integral part of the grand narrative of our ecosystem. As we continue to learn from and advocate for these creatures, we pave the way for a healthier, more balanced world—one where the harmony of nature thrives for generations to come.



