As we navigate through our daily lives, the air we breathe is an invisible yet crucial part of our environment that often goes overlooked. However, the quality of that air can have profound implications for our health and well-being. From the city streets bustling with vehicles to rural areas affected by agricultural practices, air pollution manifests in various forms, impacting our bodies and minds in ways we may not fully understand. In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between air quality and health, shedding light on how pollutants can enter our systems, the short and long-term effects they can induce, and the steps we can take to mitigate these risks. By gaining a clearer understanding of this pressing issue, we can empower ourselves to advocate for cleaner air, safeguard our health, and contribute to creating a more sustainable future. Join us as we explore the often hidden dangers lurking in the air and what they mean for you and your loved ones.
Table of Contents
- Identifying Common Air Pollutants and Their Health Impacts
- Recognizing Vulnerable Populations and Increased Health Risks
- Practical Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality
- The Role of Government Regulations in Protecting Air Quality and Public Health
- In Summary
Identifying Common Air Pollutants and Their Health Impacts
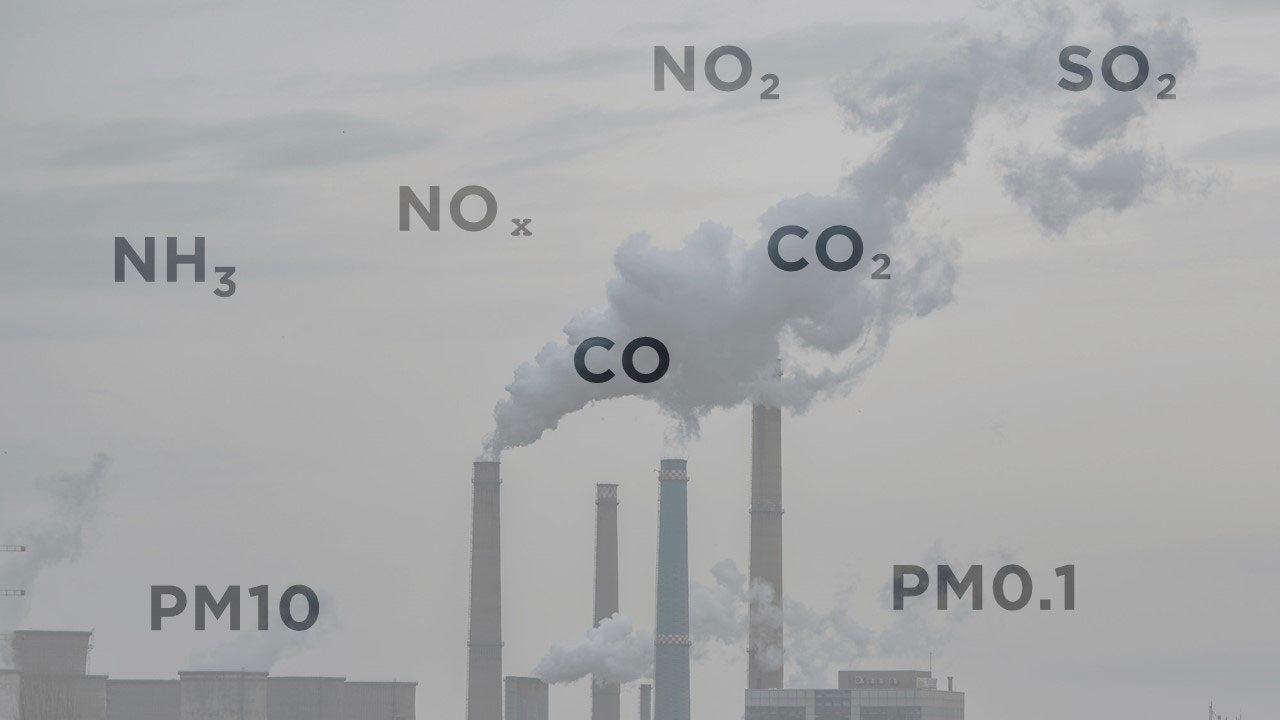

The quality of the air we breathe is crucial for our overall health, yet many people remain unaware of the harmful pollutants that often lurk in the atmosphere. Common air pollutants include particulate matter (PM), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ozone (O3). Each of these substances has distinct sources and can cause a variety of health issues. For example, particulate matter originates from vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and even natural sources like wildfires. Short-term exposure can lead to respiratory problems, while long-term exposure is linked to heart disease and lung cancer. Recognizing these pollutants is the first step towards addressing their impacts on public health.
Understanding the health effects associated with these pollutants can empower individuals and communities to take action. Here’s a brief overview of some key pollutants and their corresponding health impacts:
| Pollutant | Health Effects |
|---|---|
| Particulate Matter (PM) | Respiratory issues, heart disease, stroke |
| Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) | Worsening asthma, respiratory infections |
| Sulfur Dioxide (SO2) | Throat and lung irritation, exacerbation of asthma |
| Ozone (O3) | Chest pain, coughing, throat irritation, aggravation of lung diseases |
In addition to these pollutants, volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon monoxide (CO) also pose serious risks. VOCs are released from various household products and can lead to dizziness, headaches, and long-term neurological damage. Meanwhile, carbon monoxide, a byproduct of incomplete combustion, can be fatal at high levels due to its interference with oxygen transport in the blood. Citizens must be aware of these dangers to advocate for better air quality regulations and to make informed decisions about their exposure on a personal level.
Recognizing Vulnerable Populations and Increased Health Risks
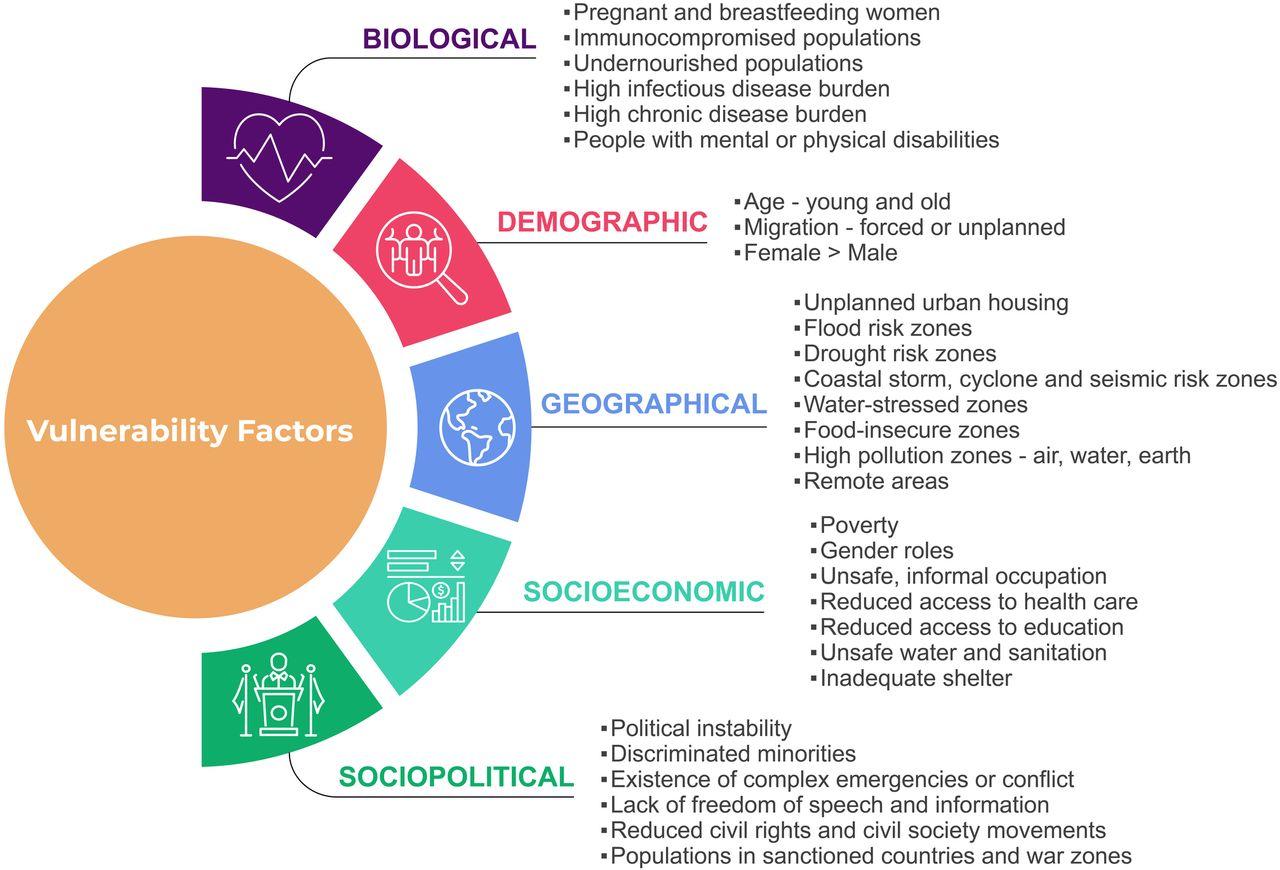
Air quality is a pressing public health issue that disproportionately affects certain groups within our communities. Vulnerable populations such as children, the elderly, pregnant women, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions face heightened risks from air pollution. Their respiratory systems and overall health can be especially sensitive to pollutants like particulate matter, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide. For example, children are not only more likely to develop asthma due to exposure to poor air quality, but their developing lungs may suffer long-lasting damage, potentially impacting their health throughout their lives. Similarly, the elderly often have compromised immune systems or existing respiratory issues, making them particularly susceptible to exacerbated health problems when air quality deteriorates.
Beyond age, socio-economic status is another critical factor that contributes to an increased vulnerability to health risks associated with poor air quality. Low-income communities often reside in areas with higher levels of pollution, due to proximity to industrial zones or major transportation routes. These communities may lack access to healthcare services or resources to mitigate exposure, compounding the health effects they experience. The table below summarizes some key health impacts linked to air quality for various vulnerable groups:
| Group | Health Impact |
|---|---|
| Children | Increased asthma rates and developmental issues |
| Elderly | Exacerbation of chronic respiratory diseases |
| Pregnant Women | Risks of low birth weight and developmental complications |
| Low-Income Communities | Higher rates of hospitalization due to respiratory issues |
Practical Strategies for Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is essential for promoting better health and well-being. One of the most effective strategies is to increase ventilation. This can be achieved by opening windows and doors to allow fresh air to circulate, or by using mechanical ventilation systems that bring in outside air. Additionally, incorporating plants into your living spaces can enhance air quality, as many houseplants naturally filter out toxins and produce oxygen. Some excellent options for indoor plants include:
- Spider Plant
- Peace Lily
- Boston Fern
- Aloe Vera
Another practical approach is to regularly maintain heating and cooling systems to prevent the accumulation of dust, mold, and allergens. This includes changing air filters and having ducts cleaned as needed. Additionally, consider implementing designated smoking areas or prohibiting smoking indoors to avoid introducing harmful substances into the air. For an even more structured plan, take a look at the following table showcasing recommended measures and their potential benefits:
| Measure | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Regular cleaning of surfaces | Reduces dust and allergens |
| Using air purifiers | Filters out pollutants effectively |
| Controlling humidity levels | Prevents mold growth |
| Minimizing VOCs | Improves overall air quality |
The Role of Government Regulations in Protecting Air Quality and Public Health
Government regulations play a crucial role in mitigating air pollution and safeguarding public health. By establishing and enforcing standards for air quality, these regulations help to minimize harmful emissions from industrial facilities, vehicles, and other sources. The Clean Air Act, for instance, mandates the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to set limits on key pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. This proactive approach not only aims to protect the environment but also ensures that vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing health conditions, are less exposed to the detrimental effects of poor air quality.
Moreover, regulations often come hand-in-hand with continuous monitoring and reporting initiatives that provide valuable data to both policymakers and the public. This transparency allows communities to assess air quality levels and understand their health implications. Effective regulations facilitate the development and promotion of cleaner technologies and transportation alternatives, leading to a significant reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. To illustrate the impact of these regulatory measures, consider the following table that highlights the decrease in particulate matter levels over the last decade in areas where strict regulations have been implemented:
| Year | Particulate Matter (PM2.5) Levels (µg/m³) |
|---|---|
| 2010 | 12.0 |
| 2015 | 9.8 |
| 2020 | 7.5 |
In Summary
understanding the intricate relationship between air quality and our health is paramount in today’s rapidly urbanizing world. The air we breathe plays a crucial role in our overall well-being, influencing everything from respiratory conditions to cardiovascular diseases and even mental health. As we navigate through daily life, it’s vital to remain aware of the air quality around us and take proactive measures to safeguard our health.
Empowering ourselves with knowledge is the first step in addressing air pollution and its effects. Simple actions—such as monitoring air quality indices, reducing emissions, and advocating for cleaner environments—can collectively lead to significant improvements in our communities. Remember, each breath we take carries with it the potential for both harm and healing. By prioritizing air quality, we not only protect our own health but also contribute to a healthier planet for future generations. So let’s commit to being informed, engaged, and active in the fight for cleaner air. Your health—and the health of those you love—depends on it. Thank you for reading, and let’s breathe better together.



