In a world marked by rapid change, where human influence often reigns supreme, nature exhibits a remarkable capacity for endurance and creativity. The story of plant adaptation unfolds like a masterful tapestry, intricately woven with threads of survival and ingenuity. From the arid deserts to the lush rainforests, plants have developed extraordinary strategies to thrive in fluctuating environments, defying the odds against drought, flood, and climate extremes. This article delves into the art of plant adaptation, exploring the ingenious mechanisms that enable these resilient organisms to navigate their challenges. Through the lens of biology and ecology, we’ll uncover the secrets of nature’s steadfastness, celebrating the myriad ways in which plants not only withstand adversity but flourish in spite of it. Join us on a journey through ecosystems alive with the vibrant colors of adaptation, where survival is not just a necessity, but a brilliant dance of evolution.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Mechanisms of Plant Adaptation in Diverse Ecosystems
- The Role of Climate Change in Shaping Plant Resilience
- Innovative Strategies for Cultivating Adaptive Practices in Gardening
- Lessons from Nature: How Understanding Plant Resilience Can Inform Conservation Efforts
- The Conclusion
Exploring the Mechanisms of Plant Adaptation in Diverse Ecosystems
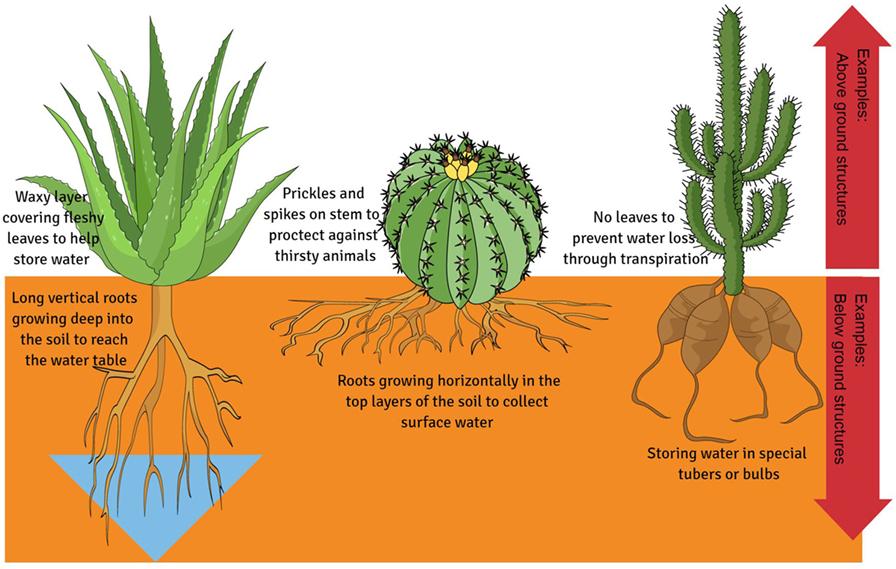
The adaptability of plants is a remarkable testament to nature’s ingenuity. In various ecosystems, plants have developed an array of strategies to thrive despite environmental challenges. Phenotypic plasticity allows them to alter their growth forms and behaviors according to the conditions they face. For instance, some species can modify their leaf size and shape to maximize photosynthesis in low-light environments, while others may develop deeper root systems during drought periods. These changes are not just reactive; they often incorporate a complex interplay of genetic expression and environmental cues, showcasing the intricate relationship between plants and their habitats.
Additionally, the mechanisms of plant adaptation can be categorized into several key processes that enhance survival across diverse landscapes. These include:
- Tolerance and Resistance: Plants develop strategies to withstand pathogens or extreme temperatures.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Mutualism with fungi or bacteria can enhance nutrient uptake and overall health.
- Seed Dormancy: Seeds may remain dormant until conditions are favorable, ensuring the continuation of the species.
In examining these adaptations, we can summarize some key traits and their corresponding ecosystems in the following table:
| Ecosystem | Adaptation Trait | Example Species |
|---|---|---|
| Desert | Water conservation through reduced leaf area | Cacti |
| Tropical Rainforest | Broad leaves for maximum light capture | Mahogany |
| Chaparral | Fire-resistant bark | Manzanita |
The Role of Climate Change in Shaping Plant Resilience
Climate change is an influential force that has dramatically altered the landscape of plant life across the globe. As environmental conditions shift due to rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and increased atmospheric carbon, plants are forced to adapt in intricate ways. The resilience of flora can be observed through various mechanisms, including:
- Phenotypic Plasticity: Some species exhibit remarkable flexibility in their physical traits, allowing them to survive in varying climates.
- Genetic Adaptation: Over generations, plants can evolve in response to shifting climatic challenges, favoring traits that enhance survival and reproduction.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Many plants establish mutually beneficial interactions with fungi and bacteria, which can improve nutrient uptake and stress resistance.
The impacts of climate change on plant resilience can be encapsulated in understanding how certain species fare better than others in shifting environments. A comparative analysis reveals that some native species are outperforming invasive counterparts in terms of survival under drought stress, showcasing their innate adaptation strategies. The table below illustrates a few plant species and their corresponding resilience traits:
| Plant Species | Adaptation Trait | Climate Resilience Level |
|---|---|---|
| Desert Willow | Deep root system | High |
| Kentucky Bluegrass | Dormancy in dry periods | Moderate |
| Coastal Sagebrush | Water-efficient stomata | High |
Innovative Strategies for Cultivating Adaptive Practices in Gardening
To cultivate a thriving garden that embraces nature’s resilience, consider integrating layers of biodiversity into your planting strategy. Companion planting involves placing mutually beneficial plants together to enhance growth and deter pests. This approach not only fosters an ecosystem teeming with life but also builds a network of adaptive practices essential for sustainability. Some effective combinations to consider include:
- Tomatoes and Basil: Basil improves the flavor of tomatoes and repels harmful insects.
- Carrots and Onions: They work as natural pest deterrents for each other.
- Cucumbers and Corn: Corn provides necessary support for climbing cucumbers while maximizing space.
Another powerful strategy is implementing permaculture principles, which focus on designing your garden to mimic natural ecosystems. This involves creating zones based on the amount of sunlight, moisture, and warding off pests through thoughtful plant placement. Utilizing natural elements such as mulched pathways and rain gardens can also help improve water retention and soil health. Consider the following attributes when planning your permaculture design:
| Element | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Mulch: | Maintains soil moisture and suppresses weeds. |
| Rain Gardens: | Captures runoff, improving drainage and supporting biodiversity. |
| Swales: | Helps manage water flow and enhances soil fertility. |
Lessons from Nature: How Understanding Plant Resilience Can Inform Conservation Efforts
Nature is a masterclass in resilience, particularly in the realm of plant life. From arid deserts to swollen wetlands, plants have developed a remarkable array of adaptations that enable them to thrive in challenging environments. Understanding these adaptations can illuminate pathways for conservation efforts, allowing us to design strategies that mimic nature’s ingenuity. For instance, the ability of certain species to alter their root systems in response to soil quality can inform agricultural practices that are ecologically sustainable. This not only enhances soil health but also fosters biodiversity, creating a more robust ecosystem. Some fascinating plant adaptations include:
- Water Storage: Succulents and cacti store water in their leaves and stems, enabling survival in arid environments.
- Leaf Structure: Plants like the lotus develop water-repellent leaves, preventing mold and promoting photosynthesis even in stagnant waters.
- Reproductive Strategies: Many plants, such as dandelions, have evolved wind-dispersed seeds, allowing them to colonize new areas rapidly.
Furthermore, the study of local flora showcases the interconnections between plant resilience and broader environmental health. The diversity of plants in a region often reflects the variety of species that coexist within that ecosystem, playing crucial roles in its stability. In an era where climate change poses unprecedented challenges, leveraging the resilience of plants can be pivotal. For example, reintroducing native plant species that have adapted over centuries to local conditions may bolster fragile ecosystems. Below is a simplified overview of plant resilience traits and their potential conservation applications:
| Trait | Description | Conservation Application |
|---|---|---|
| Stress Tolerance | Ability to survive extreme temperatures or drought | Use in reforestation projects in harsher climates |
| Rapid Growth | Fast maturation rates after disturbance | Supporting recovery in damaged ecosystems |
| Allelopathy | Release of chemicals to inhibit competitor growth | Natural weed management in conservation areas |
The Conclusion
In the intricate dance of life, plants stand as silent witnesses to the relentless passage of time and the unpredictable forces of nature. Their remarkable ability to adapt is a testament to resilience—a quality that not only allows them to survive but thrive in various environments. From the arid deserts where succulents store precious water to the frigid tundras where hardy mosses cling tenaciously to life, plants remind us that adaptability is an art form shaped by necessity.
As we reflect on the diverse strategies employed by these green marvels, we are reminded of the delicate balance that sustains our ecosystems. Each adaptation, whether subtle or striking, tells a story of endurance against the odds. In understanding these botanical techniques, we not only deepen our appreciation for the natural world but also gather invaluable insights that may influence our own approaches to challenges.
As we navigate our increasingly unpredictable environment, let us draw inspiration from nature’s resilience. The art of plant adaptation offers a blueprint for survival and a beacon of hope, illuminating the path toward a more harmonious existence with the world around us. it is a celebration of life—a tribute to the tenacity of growth, even in the face of adversity.



